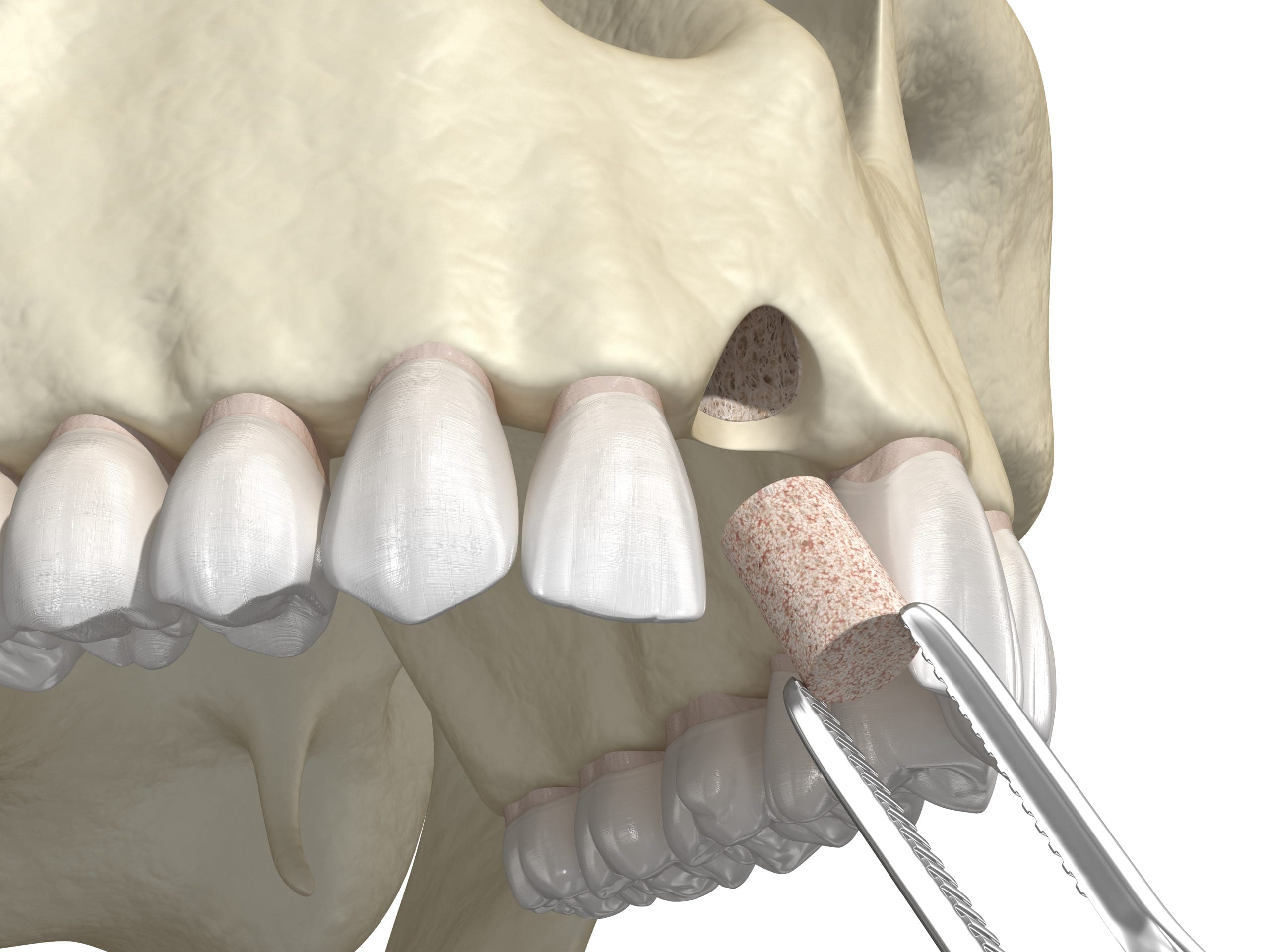
Are you curious about the different types of bone grafts and how they are used in medical treatments? Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bones to repair complex bone fractures that are extremely difficult to heal, as well as to help bones heal across damaged or removed joints. This post will provide a straightforward explanation of the various types of bone grafts, highlighting their general uses and the basic principles behind them.
Types of Bone Grafts: Autografts: Using Your Own Bone
Autografts are a popular choice among the various types of bone grafts, primarily because they utilize the patient’s own bone, typically harvested from areas like the hip, pelvis, or wrist. This method significantly reduces the risk of the body rejecting the graft since it is derived from the patient’s own tissues. Autografts are often considered the gold standard in many surgical procedures involving bone grafting due to their high success rates in terms of integration and healing. The process involves removing bone from one part of the body and transplanting it to another part where bone is deficient or needs reinforcement.
The use of autografts is particularly prevalent in procedures that require strong and quick integration of the graft with the host bone. Since the graft material is alive, containing the patient’s own living cells, it promotes faster healing and revascularization. This makes autografts an excellent option for critical or load-bearing repairs, such as those needed in spinal surgeries or major joint repairs. For more detailed information on what to expect during this process, consider reading Bone Grafting for Implants: What to Expect.
Allografts: Sourced from Human Donors
Allografts are a common choice among the various types of bone grafts used in medical procedures today. These grafts are harvested from human donors, typically processed through a bone bank, and are used to facilitate bone regeneration and repair. The process involves treating the donated bone to ensure its safety and compatibility before it can be used in another person. This type of graft is particularly valuable in complex surgeries where the patient’s own bone is insufficient for grafting purposes.
The use of allografts helps in numerous medical scenarios, ranging from dental implants to major orthopedic reconstructions. Since these grafts come from human donors, they generally have good biological compatibility, reducing the risk of rejection by the recipient’s immune system. For more detailed information on how these procedures are performed, you might consider consulting New Haven Bone Grafting Services for professional insights and services.
Xenografts: Derived from Animal Bones
Xenografts are a unique category within the various types of bone grafts, primarily sourced from animal bones. These grafts are typically harvested from species other than humans, commonly using bovine (cow) or porcine (pig) bones. The process involves treating the animal bones to ensure they are safe and biocompatible for use in human bone repair and regeneration. This type of graft is considered when autografts (bone taken from the patient’s own body) and allografts (bone taken from another human donor) are not viable options. Xenografts provide an alternative solution in the diverse field of bone grafting, contributing to advancements in medical treatments involving bone healing and integration.
Synthetic Grafts: Man-Made Materials
Synthetic grafts are a category within the types of bone grafts, primarily composed of man-made materials designed to mimic the properties of natural bone. These grafts are often used in various medical procedures to aid in bone regeneration and repair. Unlike natural bone grafts sourced from human or animal donors, synthetic options provide an alternative that reduces the risk of disease transmission and immune rejection. They are engineered to support bone growth and integration at the site of implantation, making them a crucial tool in reconstructive surgeries. For those seeking further information on how these innovative solutions are applied in dental procedures, the New Haven Dentist at New Haven Dental Center Family & Cosmetic Dentistry can provide insights based on their professional experience.
Composite Grafts: Multiple Source Materials
Composite grafts are a notable category within the various types of bone grafts, distinguished by their utilization of multiple source materials. These grafts combine different elements, such as autografts, allografts, and synthetic materials, to leverage the unique benefits of each. This integration aims to optimize the structural and biological properties necessary for successful bone regeneration and healing. Composite grafts are often used in complex or challenging bone repair situations where a single material might not suffice.
Demineralized Bone Matrix: Processed Bone
Demineralized Bone Matrix (DBM) is a popular choice among the various types of bone grafts due to its unique processing method and effectiveness in facilitating bone growth. DBM is created by removing the mineral content from donor bones, which leaves behind a collagen-rich matrix. This matrix contains growth factors that are essential for bone regeneration, making it highly effective for use in surgeries requiring bone grafts, such as spinal fusion and joint reconstruction. Its versatility and proven results make DBM a critical component in the array of options available for bone grafting procedures.
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins: Growth Factors
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs) are crucial growth factors that play a significant role in the types of bone grafts used for various medical procedures. These proteins are naturally occurring substances in the body that promote the formation of new bone tissue. BMPs are particularly useful in orthopedic and dental surgeries where bone regeneration is essential. By stimulating key cells involved in bone formation, BMPs enhance the healing process, making them a vital component in advanced bone grafting techniques. This innovative approach helps ensure successful outcomes in bone repair and reconstruction, highlighting the evolution and effectiveness of modern bone graft options.
Ceramic-Based Grafts: Biocompatible Options
Ceramic-based grafts are a significant category within the various types of bone grafts, offering unique advantages due to their biocompatibility with human tissues. These grafts are primarily composed of calcium phosphates, which are similar to the mineral component of bone, making them an excellent option for facilitating bone regeneration and repair. Their porous nature allows for new bone growth through the graft, integrating seamlessly with the existing bone structure. Ceramic-based grafts are particularly favored in orthopedics and dental implantology for their ability to support bone regrowth without causing immune reactions, making them a safe and effective choice for patients needing bone reconstruction.
Polymer-Based Grafts: Synthetic Choices
When exploring types of bone grafts, polymer-based grafts stand out as a synthetic option favored for their versatility and effectiveness in bone repair and regeneration. These grafts are engineered from biocompatible polymeric materials, which can be designed to mimic the structure and function of natural bone. They are particularly useful in cases where the patient lacks sufficient natural bone tissue for grafting. Polymer-based grafts not only support new bone growth but also degrade gradually, making them an excellent choice for maintaining long-term structural integrity and promoting natural bone healing processes.
Conclusion
We hope this overview has helped clarify the different types of bone grafts. For further inquiries, feel free to call us at 260-748-3696 or read our reviews on Google Maps.